java基础-常用API&异常
黑马2022资料阶段一:java基础-第六章
4-1 String类
03-概述
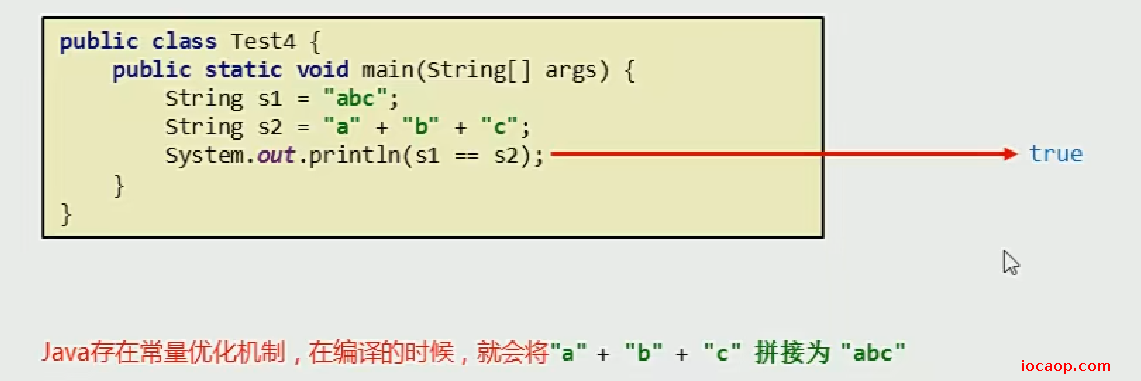
java程序中,所有双引号字符串都是String类对象。
字符串是常量,创建后不能更改。
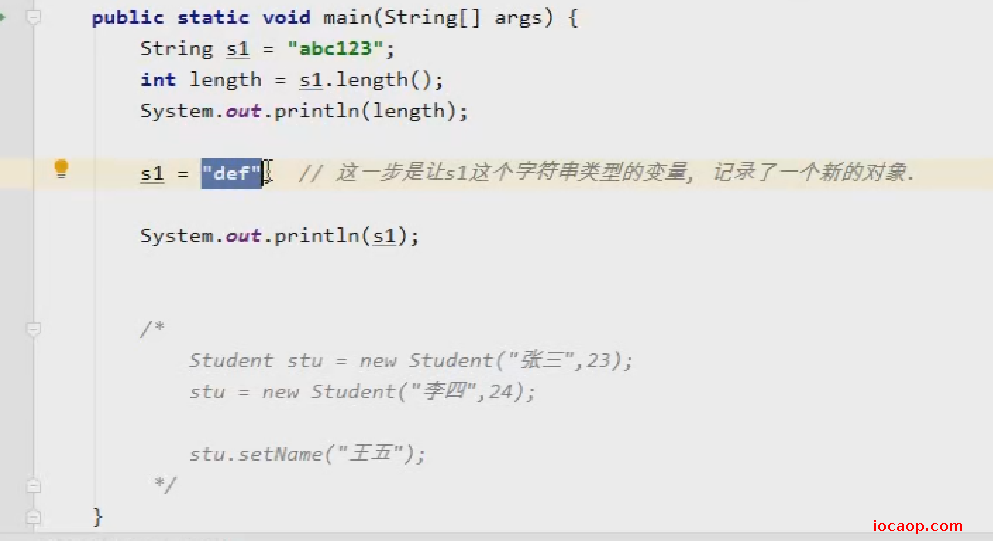
String类内部有一个char[],没有提供set方法给我们修改内存。上图代码中,只是讲栈内存中的s1变量指向了一个新的String类对象。
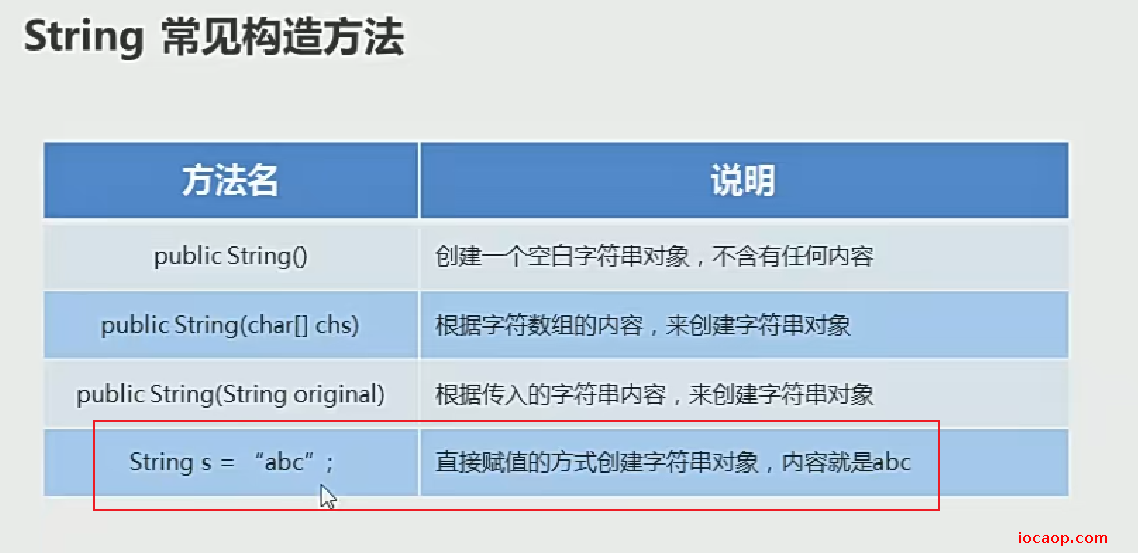
04-String类的常见构造
05-创建字符串对象的区别对比
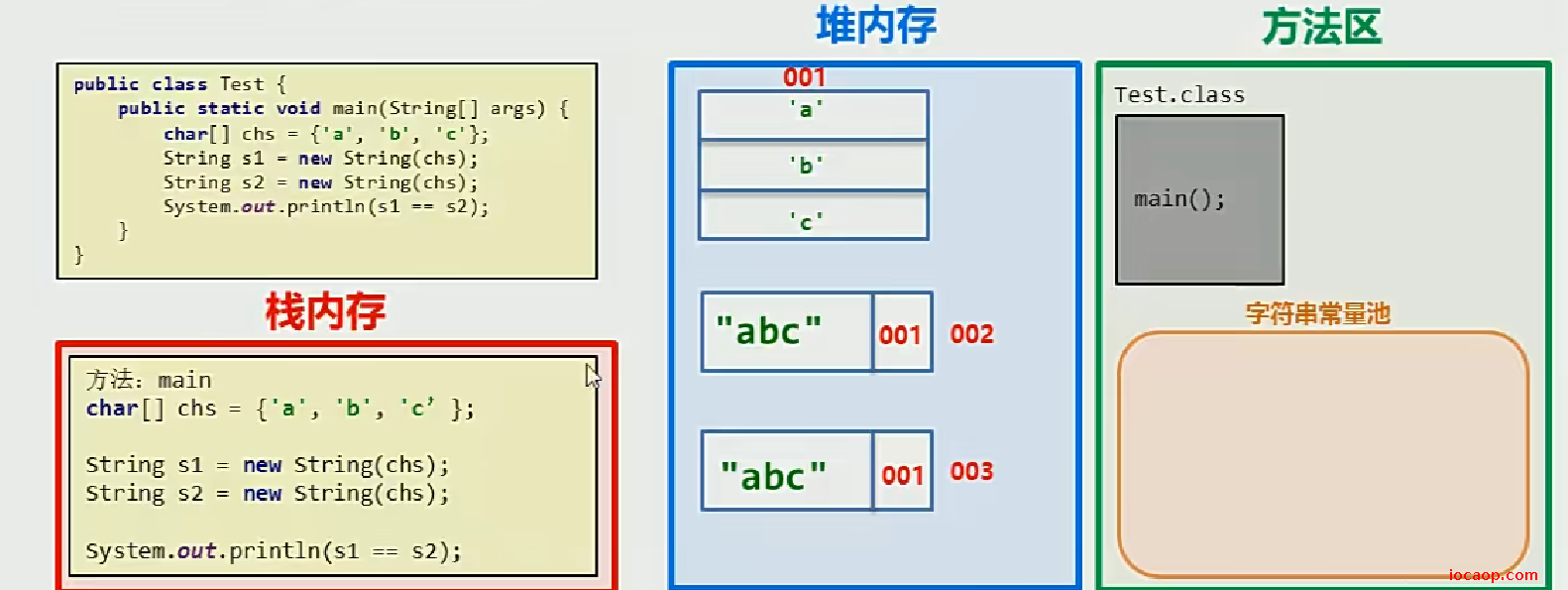
构造方法可以创建String对象,双引号也能直接创建字符串对象,有什么区别?
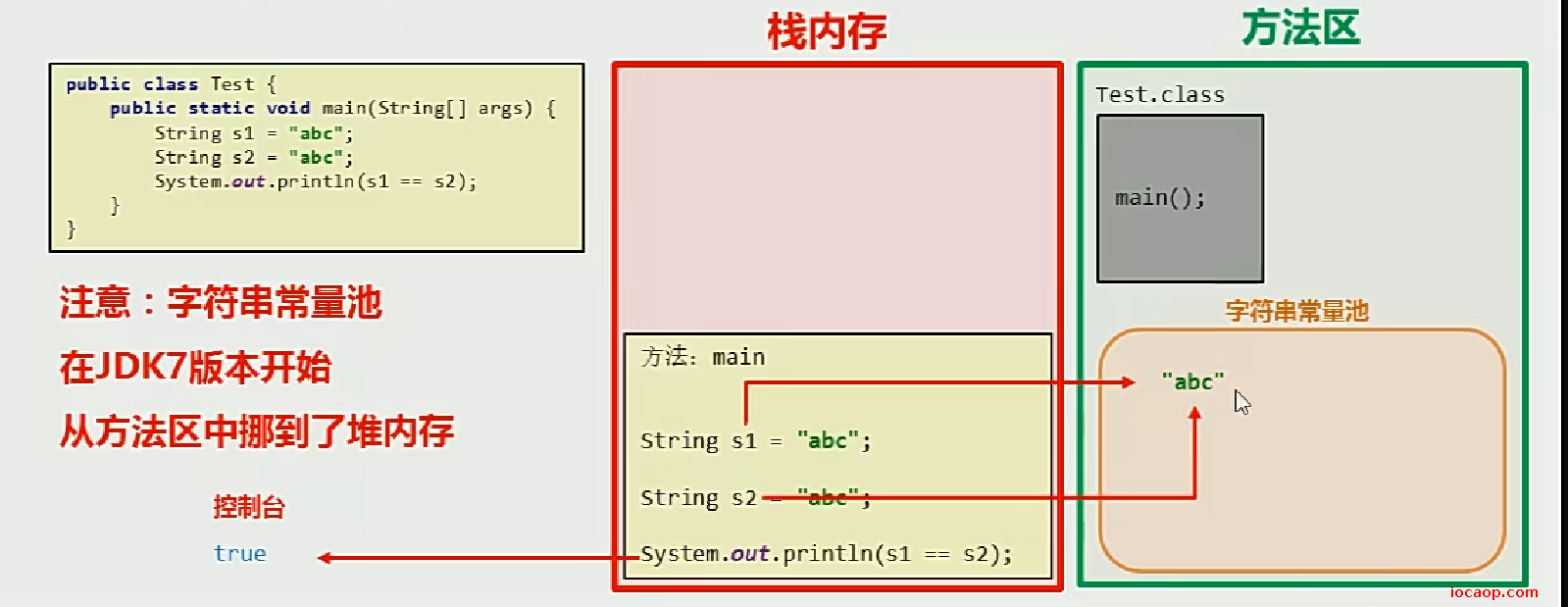
首先复习一下==比较,基本数据类型时比较的是值,引用数据类型比较的是地址。

以双引号方式给出的字符串,只要字符序列相同(顺序和大小写),无论在代码中出现多少次,JVM都只会创建一个String对象,并在字符串常量池中维护。
字符串常量池:当使用双引号创建字符串对象的时候,系统会检测该字符串是否在常量池中存在,如果存在则复用,不存在才创建。
06-String类常见面试题
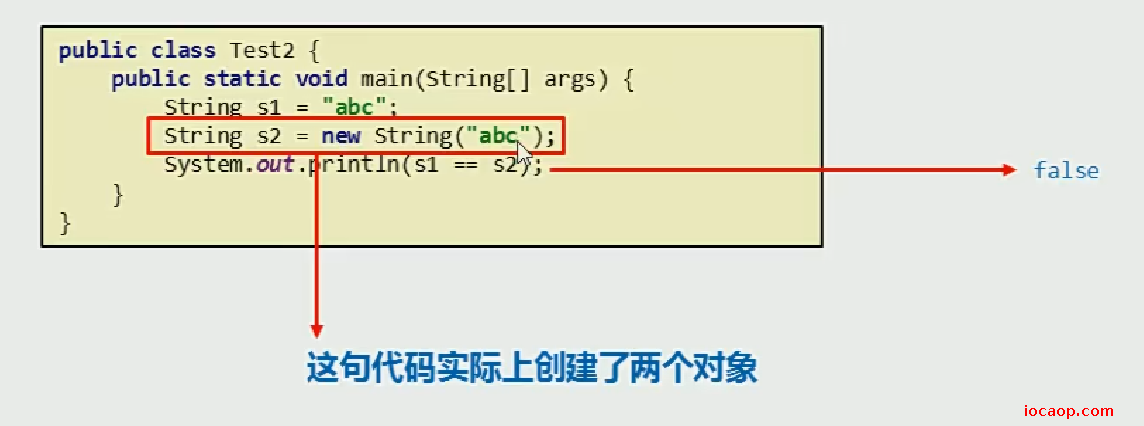
为什么是2个?new一个,字符串"abc"本身是一个。
Java 语言提供对字符串串联符号("+")以及将其他对象转换为字符串的特殊支持。字符串串联是通过 StringBuilder或 StringBuffer类及其 append 方法实现的
4-2 StringBuilder
15-概述
概述:可变字符串类,可以看做是一个String的容器。
学他干嘛:提高字符串操作效率。方法抽取快捷键ctrl+alt+m
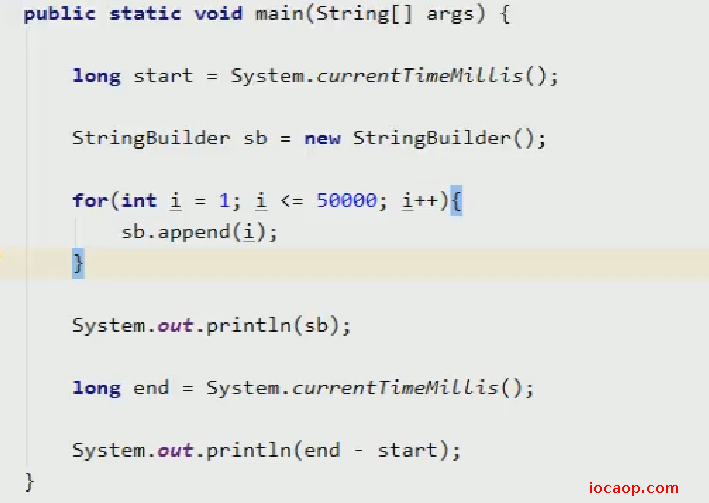
String拼接:2933ms

StringBuilder拼接:294ms
16-常用构造


17-常用成员方法
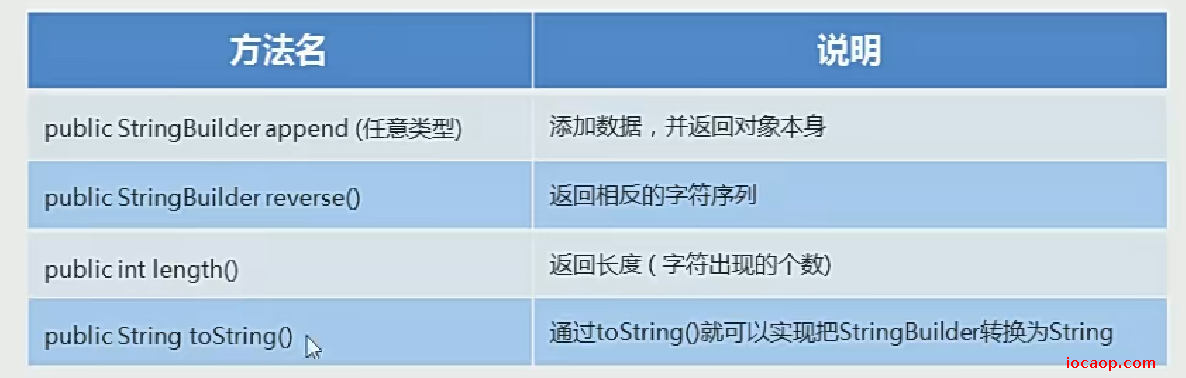

append方法调用后返回的是调用该方法的StringBuilder对象的本身,所以可以链式调用。
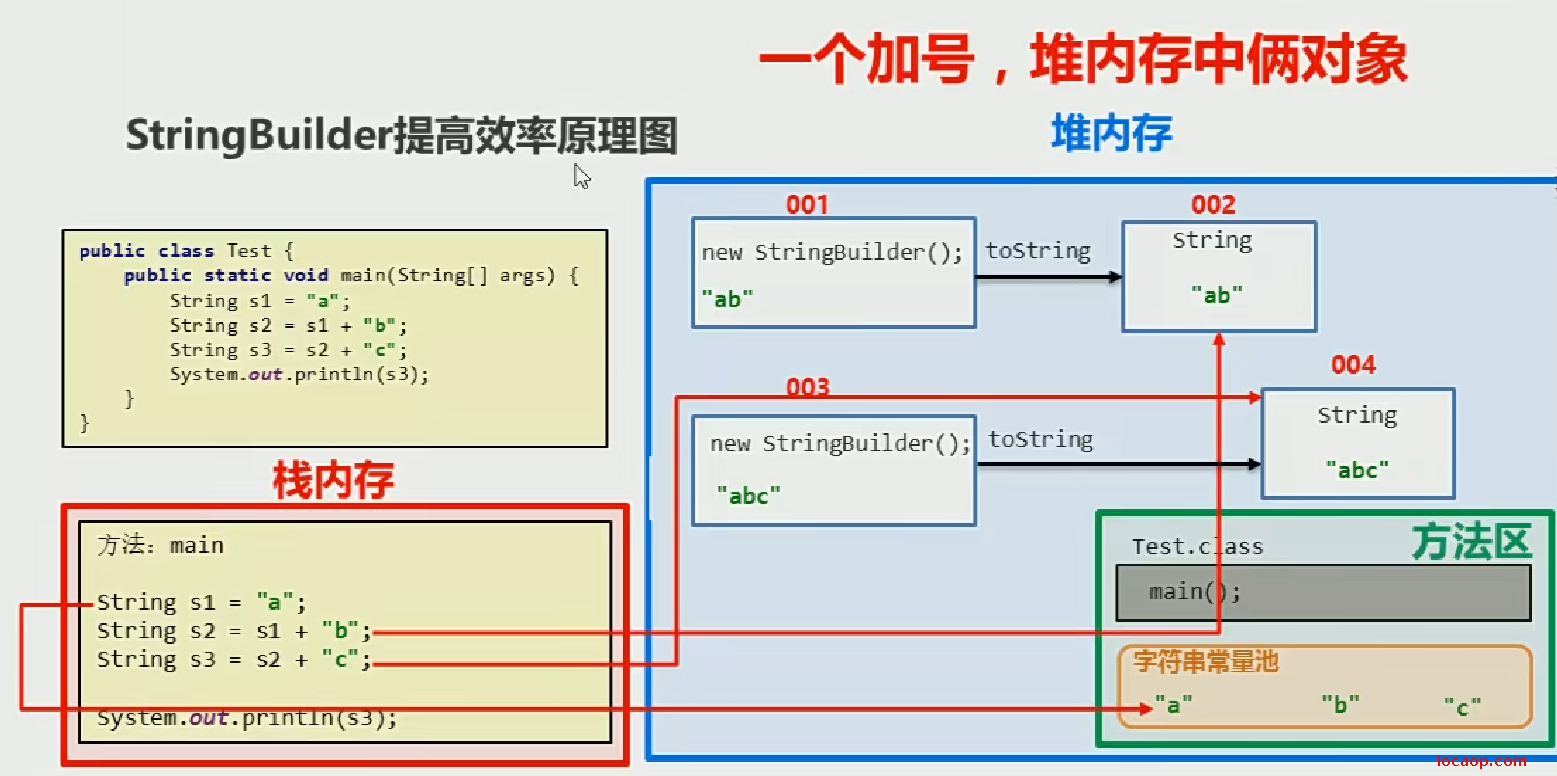
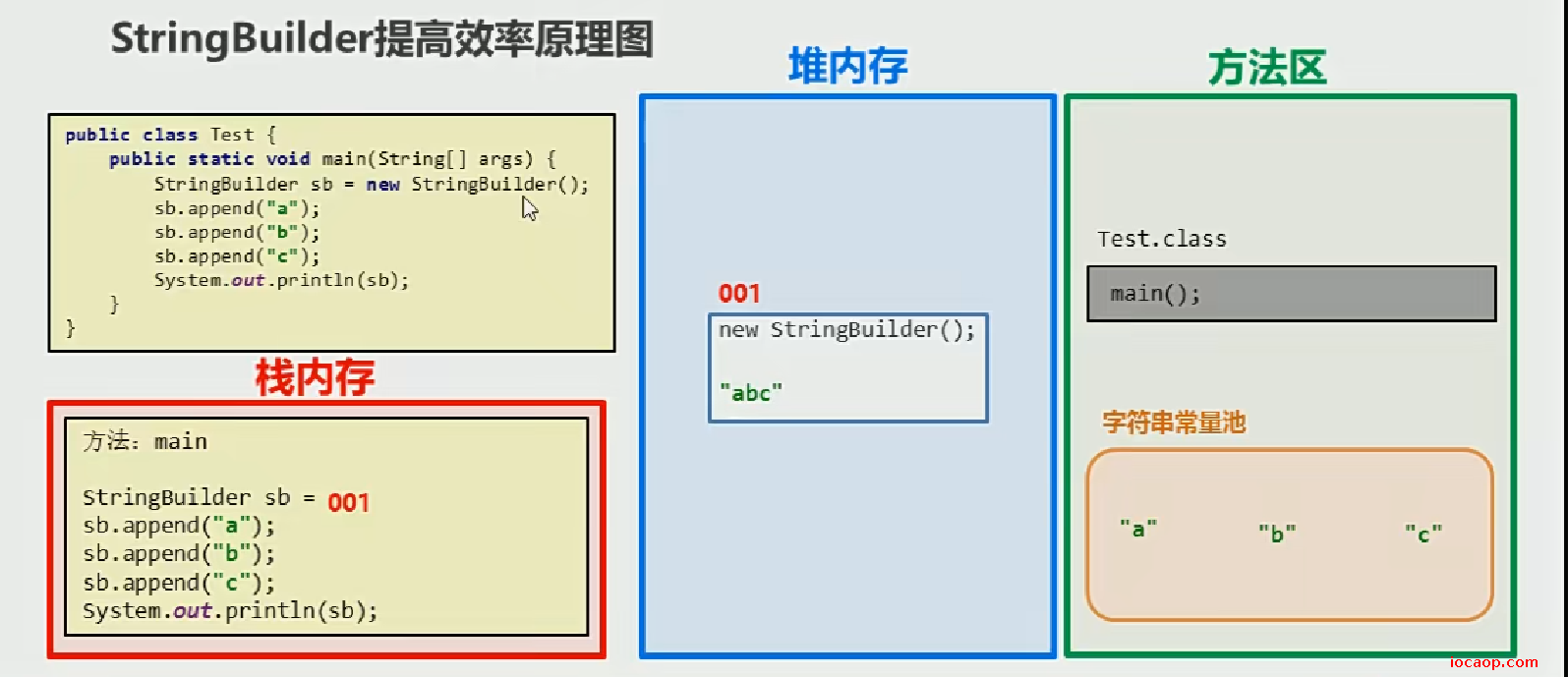
18-StringBuilder提高效率的原理图
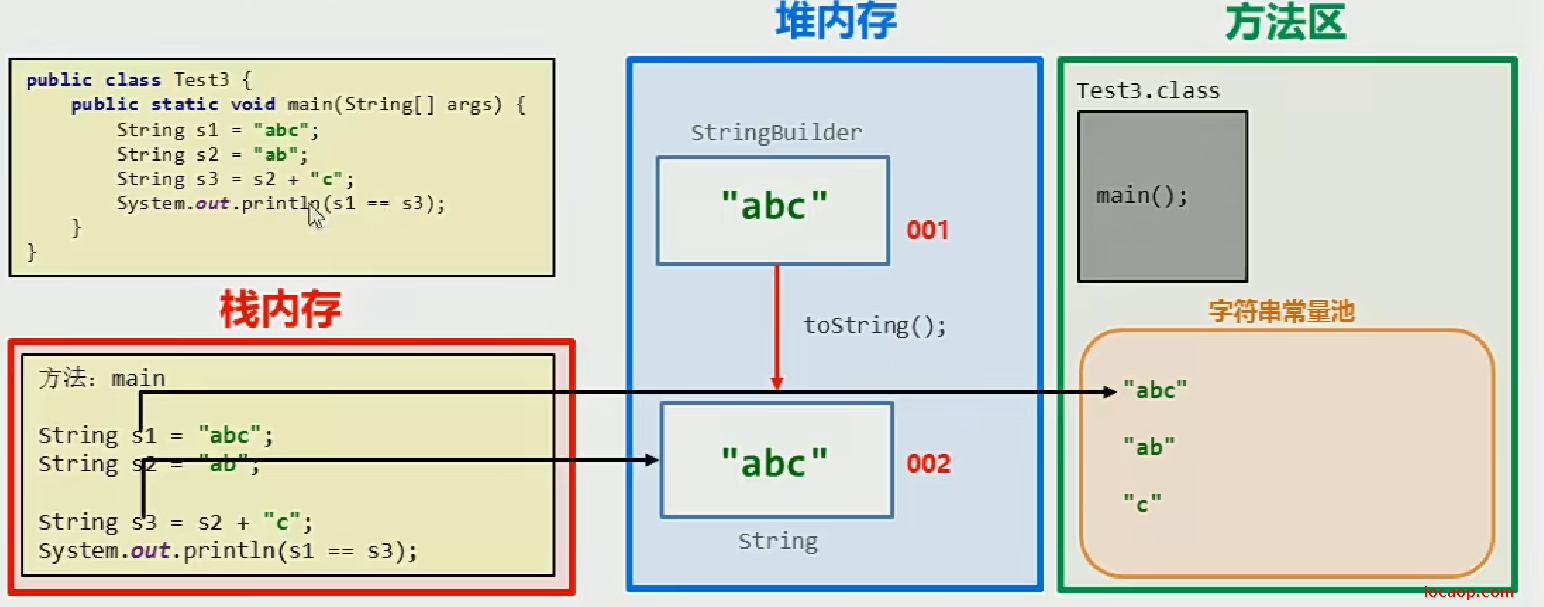
不用StringBuilder,用加号拼接,每次加号都会创建一个StringBuilder对象和一个String(因为接收的引用类型是String,所以会自动调用toString()方法)对象
使用加号后,只会有一个StringBuilder对象,需要使用String,调用toString()方法即可
5-1 ArrayList
01-为什么用集合?
数组不能动态改变大小,需要增加新数据时不能动态扩容。
集合特点:提供存储空间可变的存储模型,存储的数据容量可以发生改变。
集合和数组的区别:
- 共同点:都是存储数据的容器
- 不同点:数组的容量是固定的,集合的容量是可变的。
02-ArrayList的构造方法和添加方法
简介:List接口的可调整大小的数组实现。实现所有可选的列表操作,并允许所有元素,包括null。除了实现List接口之外,该类还提供了一些方法来操作内部用于存储列表的数组的大小。(该类大致等同于Vector,只是它是非同步(线程不安全)的。)
构造方法:
| 构造方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList() | 构造一个初始容量为10的空列表。(当超过容量时会自动扩容) |
| ArrayList(int initialCapacity) | 指定容量 |
| ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) | 按照集合的迭代器返回的顺序构造一个包含指定集合元素的列表。 |
泛型如果不写,默认Object。

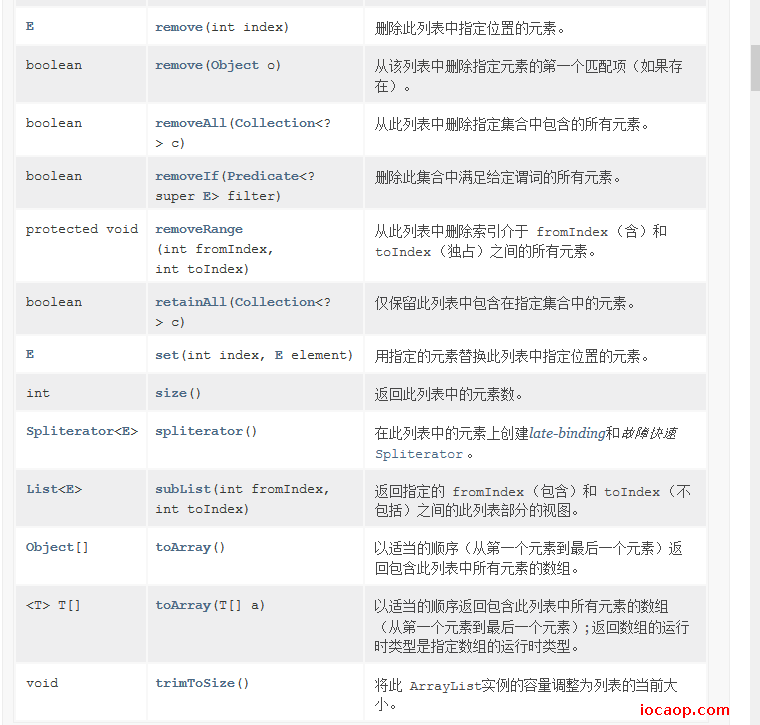
8-1API的基本使用与Object类
06-Object面试题
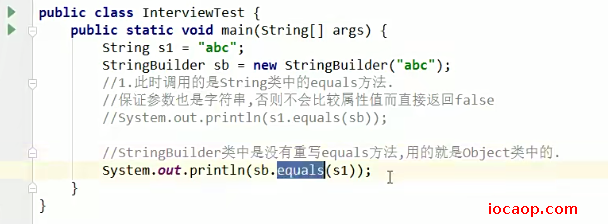
07-Objects方法
第二个头String方法,先判断参数1中的对象是否为null,不为空返回对象的toString(),为空则返回第二个参数的值。
08-BigDecimal构造
想要精确计算,应该使用字符串构造,不然还是会不精确。
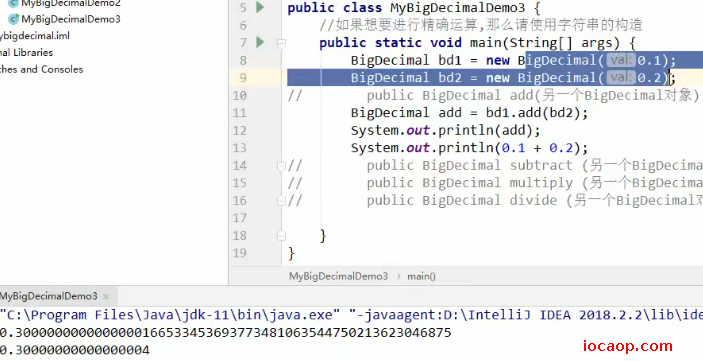
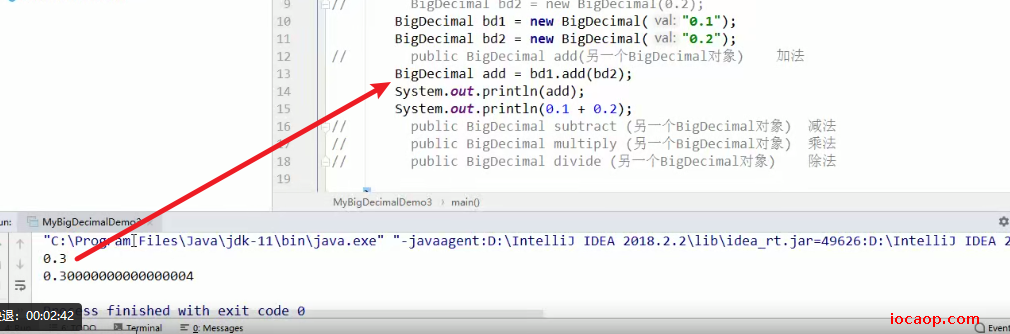
10-BigDecimal特殊方法
BigDecimal是精确计算,如果出现除不尽的情况,会报错。需要手动指定。


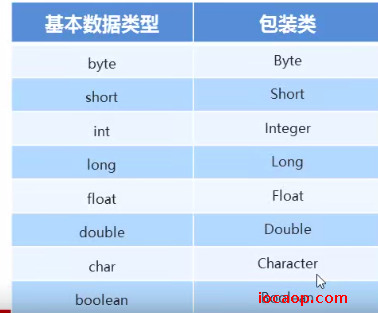
11-基本数据类型包装类
就是将基本类型包装成类。
好处:可以在对象中定义更多功能方法操作该数据。
常用操作,基本数据类型和字符串之间的转换。
12-Integer获得对象
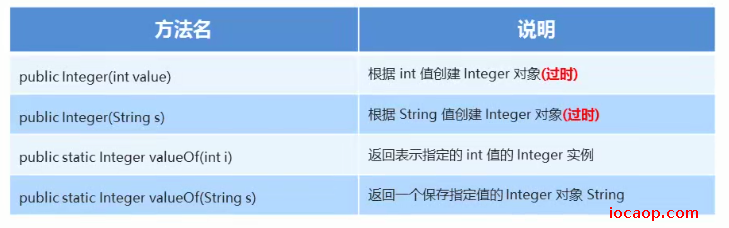
13-Integer自动装箱和自动拆箱
自动装箱:把一个基本数据类型变量对应包装类的时候(Integer i = 1;),java底层会自动帮我们调用valueOf方法,创建Integer对象。
自动拆箱:把一个包装类变成基本数据类型(int i2 =i)
需要注意的是,包装类型也是对象,在使用时需要进行非null判断。
14-Integer类型转换

16-数组的高级操作-二分查找思路分析
二分查找的前提条件:数组的元素需要按顺序排序好
元素存在-要查值为3的索引。
思路:定义两个变量min和max,确定查找的范围。根据min和max计算中间点的位置,公式:mid = (min+max)/2(整数),假设min是0,max是9,mid就是4。
- min是0,max是9,mid为4,大于3,所以后面的不需要了,max为mid-1=3
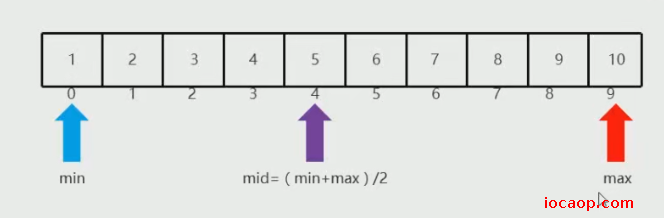
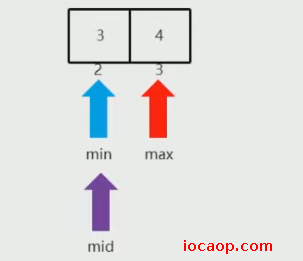
min是0,max是原来的mid-1等于3,mid是1,小于3,所以前面的不要了,min等于mid+1=2
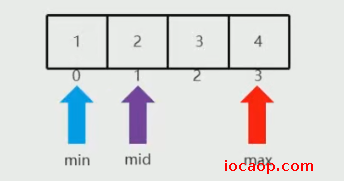
min是2,max是3,mid是2,等于3,二分查找结束。
元素不存在-查找值为11的元素索引
min是0,max是9,mid是4,值5小于11,所以左边的不要了,min改为mid+1=5
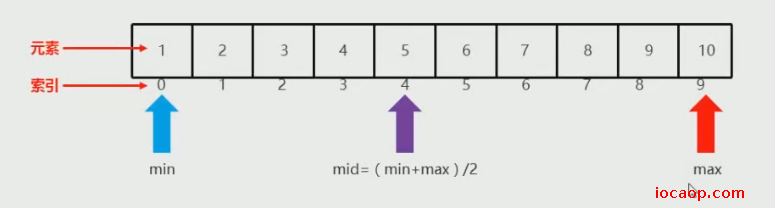
min是5,max是9,mid是7,值8小于11,左边不要了,min改为mid+1=8
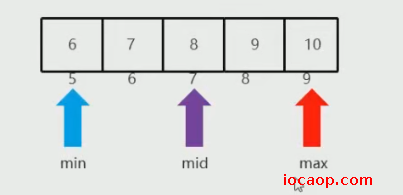
min是8,max是9,mid是8,值9小于11,左边不要了,min=mid+1=9
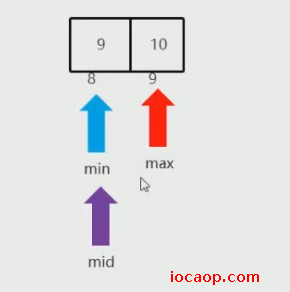
min=max=mid=9,值10小于11,左边不要了,min=mid+1=10
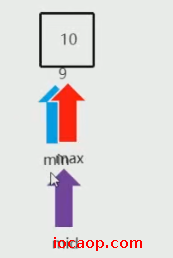
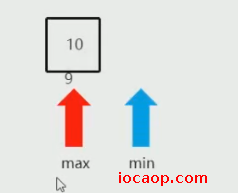
min是9,max是10,可以发现,min大于max,这时可以认为查询的元素不存在。
17-数组的高级操作-二分查找代码实现
/**
* 二分查找
*
* @author lzc
* @date 2023/04/20
*/
public class BinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 待查找的数组
int [] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
// 待查找的元素
int number = 3;
int index = binarySearchMethod(arr,number);
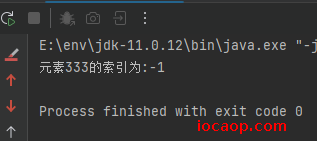
System.out.println("元素"+number+"的索引为:"+index);
}
private static int binarySearchMethod(int[] arr, int number) {
// 确定查找的范围
int min = 0;
int max = arr.length -1;
// 查找的条件 min<max 否则就是没找到
while (min <max){
// 计算中间位置 位运算 右移一位就是除以2
int mid = (min+max)>>1;
// 分三种情况,在左边、在右边、找到了
if (arr[mid]>number){
// 在左边,右边的不要了,最大索引范围为中间位置左边一个
max = mid - 1;
}else if (arr[mid]<number){
// 在右边,左边的不要了,最小索引范围为中间位置右边一个
min = mid + 1 ;
}else if (arr[mid] == number){
return mid;
}
}
// 没找到直接返回-1
return -1;
}
}
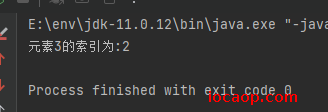
运行测试:
18-数组的高级操作-冒泡排序思路分析
相邻的数据两两比较,小的放前面,大的放后面。
初始数据: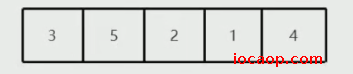
期望数据: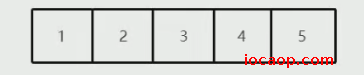
相邻的两个元素比较,把小的放左边,大的放右边。
第一轮:可以把最大的冒泡到最右边
【3 5 2 1 4】
3 2 5 1 4
3 2 1 5 4
3 2 1 4 5
第二轮:把第二大的冒泡
【3 2 1 4】 5
2 3 1 4 5
2 1 3 4 5
第三轮
【2 1 3 】4 5
1 2 3 4 5
第四轮
【1 2 】3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
总结:如果有n个元素需要进行排序,则需要进行n-1轮冒泡,每轮冒泡需要比较n-i次。i为第几轮。
19-数组高级操作-冒泡排序代码实现
/**
* 冒泡排序
*
* @author lzc
* @date 2023/04/21
*/
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] arr = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
bubbleSort(arr);
}
private static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i=1;i<arr.length-1;i++){
for (int j = 0;j<arr.length-i;j++){
if (arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
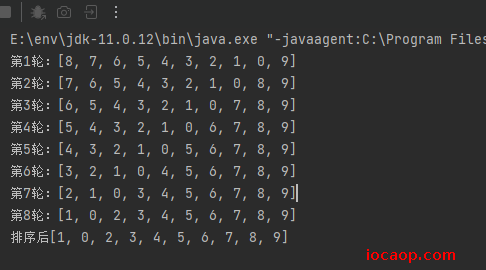
System.out.println("第"+i+"轮:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
}
System.out.println("排序后"+Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
为了更直观,打印最差的情况:
20-递归-概念
概述:方法定义中调用方法本身的现象。
思路:把复杂问题转为一个与原问题相似的规模较小的问题来求解,递归策略只需少量的程序就可以描述出截图过程所需要的多次重复计算。
递归解决问题要找到2个内容:
- 递归出口:否则会出现内存溢出
- 递归规则:与原问题相似的规模较小的问题
求1-100的和:
/**
* 求1-100 传统写法
*
* @author 赖卓成
* @date 2023/04/23
*/
public class MyFactorialDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
/**
* 求1-100 递归写法
*
* @author 赖卓成
* @date 2023/04/23
*/
public class MyFactorialDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = getSum(100);
System.out.println(sum);
}
private static int getSum(int i) {
if (i==1){
return 1;
}else {
return i+getSum(i-1);
}
}
}
21-递归-求阶乘代码实现
需求:用递归求5的阶乘,输出结果。
5! = 5*4*3*2*1
- 递归的出口 1!=1,也就是一直拆分,直到乘1为止。
- 递归规则:n!=n*(n-1!),如5的阶乘等于5乘以4的阶乘:5!=5*4!
代码实现:
/**
* 用递归求5的阶乘 5*4*3*2*1 = 120
*
* @author lzc
* @date 2023/04/25
*/
public class MyFactorialDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = getResult(5);
System.out.println(result);
}
private static int getResult(int i) {
// 递归出口
if (i==1){
return 1;
}
// 递归的规则 n! = n*(n-1)!
return i * getResult(i-1);
}
}
22-递归-内存图
上面的代码,如果递归没有出口,会发生什么?
栈溢出:
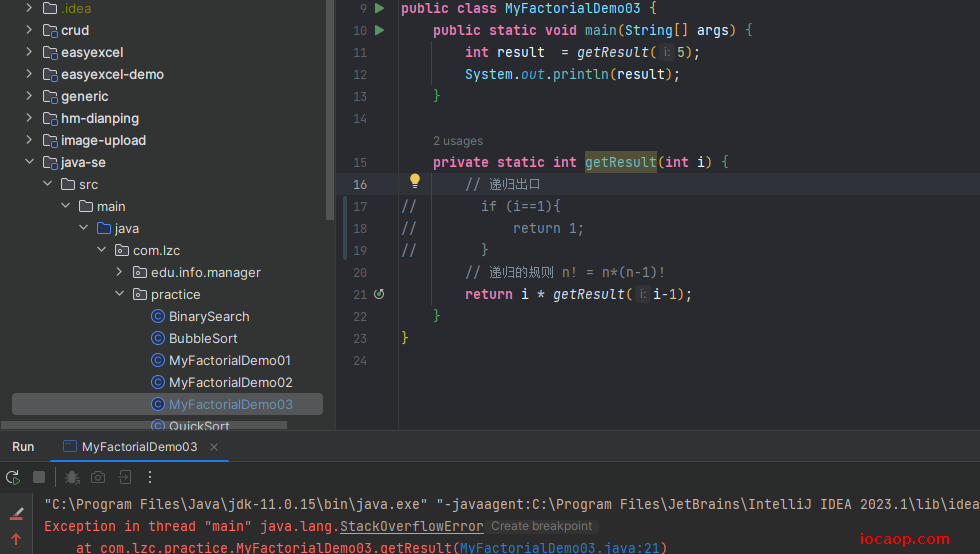
找递归规则的技巧:下一次调用一定比本次调用更靠近出口。
栈内存:

每次方法调用会压栈,调用结束返回时弹栈。如果递归没有出口,会一直调用,导致栈内存溢出。
返回时如图:颜色标记
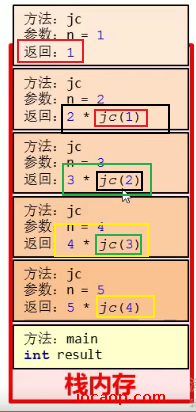
23-数组的高级操作-快排核心思路分析
- 在冒泡排序中一次循环结束,就确定了最大值和最大值的位置
- 快速排序中,每次递归都以第一个数为基准数,找到数组中所有比它小的数和所有比它大的数,小的放左边,大的放右边,来确定基准数的位置。
假设有下面乱序的数组:
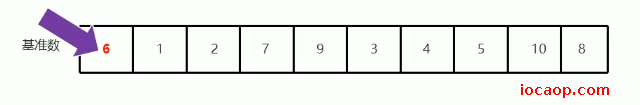
在一次递归后,应该会确定基准数6应该在数组的位置,且它左边的数都比他小(顺序不管),它右边的数都比他大(顺序不管)。
从右开始找,所以定义一个变量指向数组最大索引,开始找比6小的,找到后就停下来,不移动索引。第一次找到5比6小,停下来:
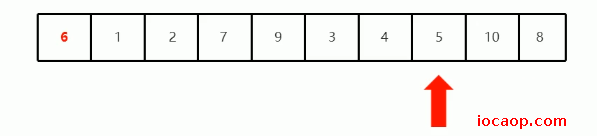
停下来后,就从左边开始找比6更大的,也是定义一个变量记录索引位置,第一次找到7比6大,停下来,
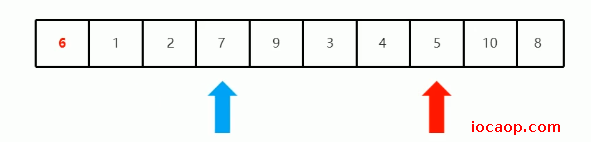
交换两个索引位置的值:
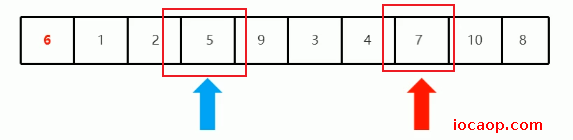
交换完后,按照上面的方式继续找,从左边开始移动,找比6大的,从右变开始移动,找比6小的,第一次,找到4比6小,停下来:
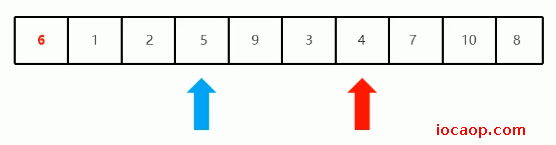
停下来后,从左边开始移动,找比6大的,第一次找到9,停下来:
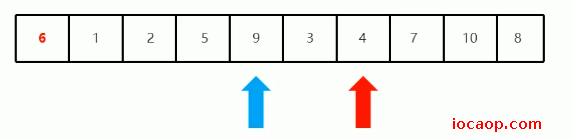
交换位置:
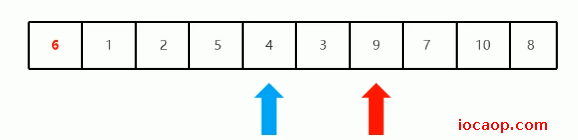
交换完,再从右变开始找比6小的,找到3,停下来:
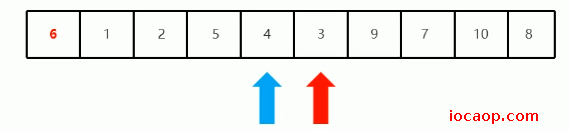
停下来后从左往右找,发现两个索引变量重叠了:
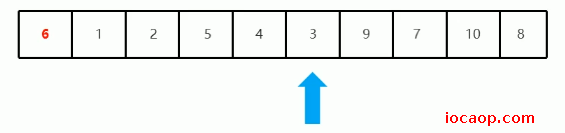
当两个索引变量重叠后,基准数归位,也就是把基准数和当前索引位置的值交换:
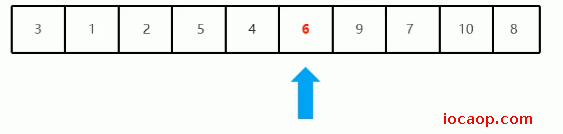
到此,一次递归结束,就确定了第一个基准数应该放的位置。
24-数组的高级操作-快排核心代码实现
先实现一次递归,基准数6在数组中应该存放的位置。
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义数组
int[] arr = {6, 1, 2, 7, 9, 3, 4, 5, 10, 8};
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
// 一次递归后,结果应该是确定了基准数6应该处于哪个位置,且左边的比6小,右边的比6大
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* 快速排序 一次递归
*
* @param arr 数组
* @param left 最小索引
* @param right 最大索引
*/
private static void quickSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
// 从一次递归的最后一步,即两个索引重叠时可以得出循环次数:
while (left != right) {
// 从右往左找比基准数小的,可以得出以下循环,即:没找到一直移动索引,循环次数就是移动次数。找到了就停下来,即跳出循环
while (arr[0] <= arr[right] && left < right) {
right--;
}
// 上一个循环,从右往左找到比6小的,找到后停下来,就要移动左边索引,从左往右找比6大的,没找到就一直移动索引
while (arr[0] >= arr[left] && left < right) {
left++;
}
// 走到这一步,说明从右往左已经找到比6小的,从左往右也已经找到比6大的,此时交换两个索引位置的值
int temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[right];
arr[right] = temp;
}
// 两个索引重叠时,基准数归位,即交换基准数和当前索引位置的值
int temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[0];
arr[0] = temp;
}
}
需要注意,在移动指针后,需要处理等于的情况。即:这里遗留一个问题,即使元素没重复,不加=依然是错的,没找到原因。
// 处理等于的情况 <=
while (arr[0] <= arr[right] && left < right){...}
// 处理等于的情况 <=
while (arr[0] >= arr[left] && left < right){...}
递归一次后,记得把基准数归位。
经过调试,发现问题,在做比较时,左指针left初始为0,也就是拿arr[0]和基准数自己比较了一次,导致了交换。
解决:要么加上= ,要么初始指针+1。
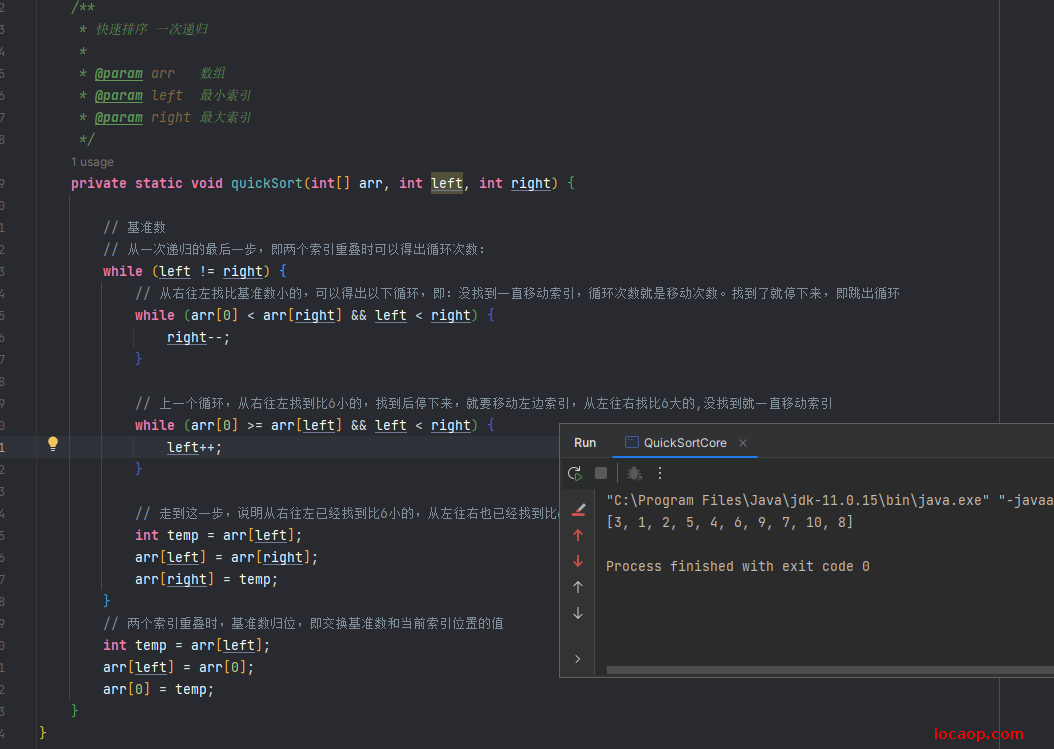
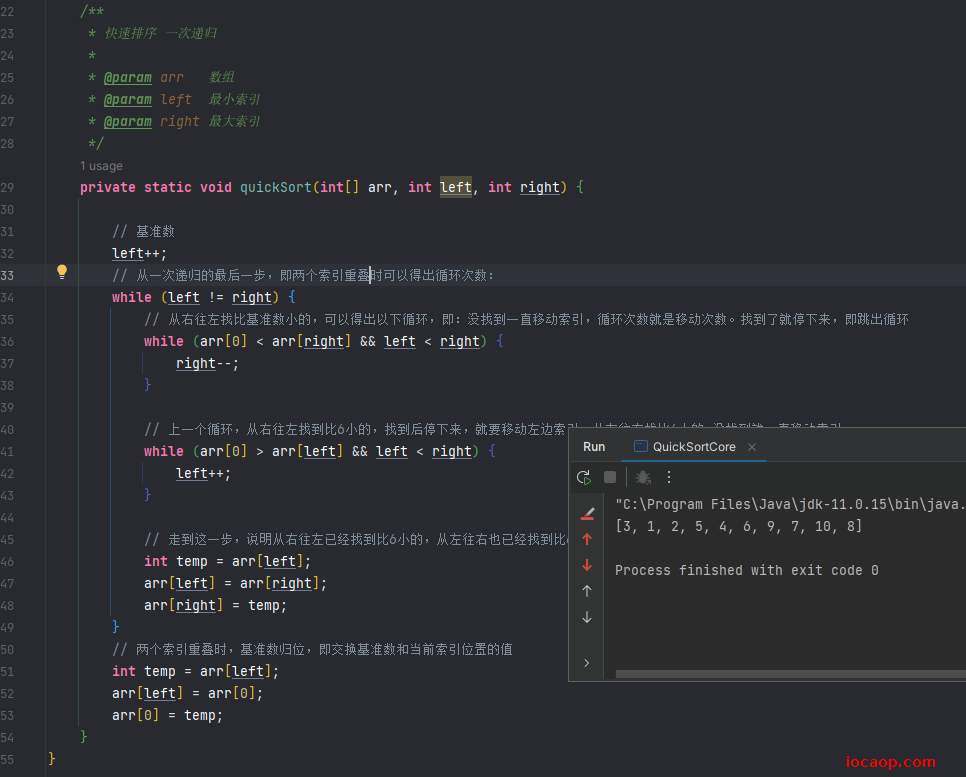
25-数组的高级操作-快排完整实现
上面代码,也就是快排中的代码只调用一次后,形成的效果如下图:
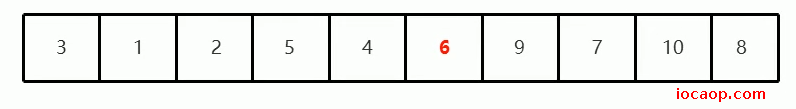
接下来我们就要再次选取基准数,确定基准数位置,我们选择下标为0的,也就是3为基准数,在整个范围中来确定它的位置。
依然是从右往左找,即arr[arr.length-1]开始,即最右的位置往左移动,遇到比3小的则停下来,再从左往右找到比3大的数停下来,左交换。
不难发现,经过第一次循环操作,现在根本不需要从最右边开始找,因为6右边的都大于6,左边都小于6,可以得到0索引的值小于6,即3<6,而6右边都大于6,得6右边都大于3。
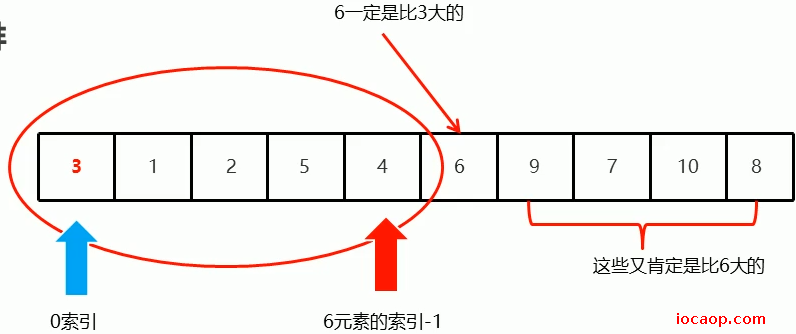
右边的也是同理:
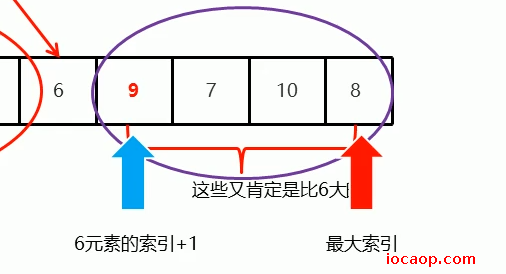
什么时候递归结束?
当3元素位置确定后,下一次需要递归的范围如下图:
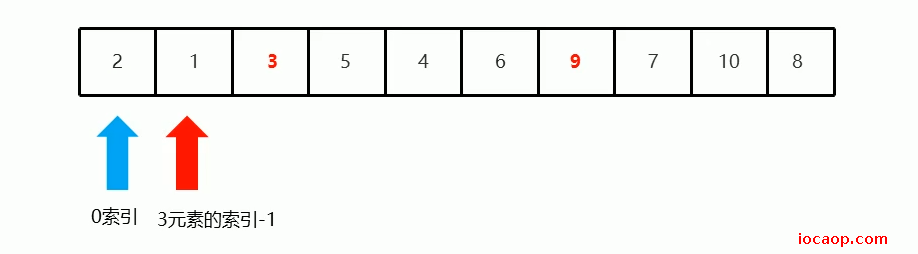
再确定2元素的位置,得下一次需要递归将基准数归位的范围:
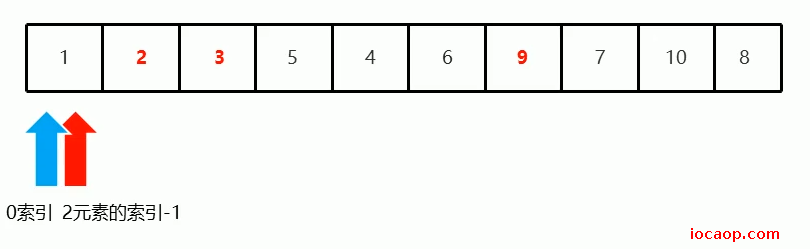
1元素位置确定后,下一次基准数归位需要递归的范围:
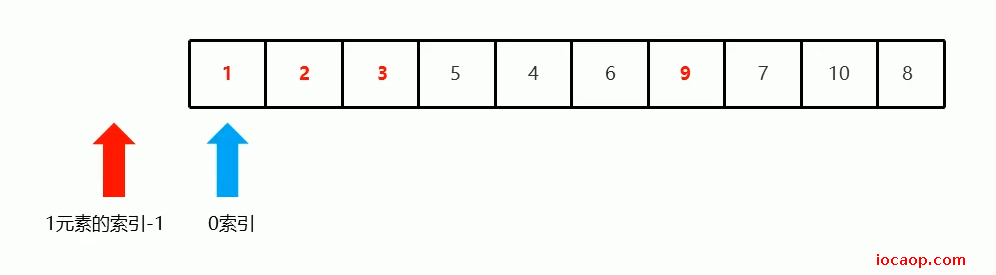
可以看到,数组越界了,这时候应该结束递归了。即left>right时结束递归。
代码实现:
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义数组
int[] arr = {6, 1, 2, 7, 9, 3, 4, 5, 10, 8};
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
// 一次递归后,结果应该是确定了基准数6应该处于哪个位置,且左边的比6小,右边的比6大
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* 快速排序 一次递归
*
* @param arr 数组
* @param left 最小索引
* @param right 最大索引
*/
private static void quickSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
if (left>right){
return;
}
int left0 = left;
int max = right;
int baseNumber = arr[left0];
// 从一次递归的最后一步,即两个索引重叠时可以得出循环次数:
while (left != right) {
// 从右往左找比基准数小的,可以得出以下循环,即:没找到一直移动索引,循环次数就是移动次数。找到了就停下来,即跳出循环
while (baseNumber <= arr[right] && left < right) {
right--;
}
// 上一个循环,从右往左找到比6小的,找到后停下来,就要移动左边索引,从左往右找比6大的,没找到就一直移动索引
while (baseNumber >= arr[left] && left < right) {
left++;
}
// 走到这一步,说明从右往左已经找到比6小的,从左往右也已经找到比6大的,此时交换两个索引位置的值
int temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[right];
arr[right] = temp;
}
// 两个索引重叠时,基准数归位,即交换基准数和当前索引位置的值
int temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = baseNumber;
arr[left0] = temp;
// 递归处理左边
quickSort(arr,left0,left-1);
// 递归处理右边
quickSort(arr,left+1,max);
}
}
这里,进入方法时判断递归条件,定义了left0和max记录基准数位置和递归索引最大值。为什么要这样?因为基准数位置不是每次都是0索引,当确定第一次递归,即6元素右边的元素的范围时,基准数位置每次都在变化。至于max,范围有不一样的情况,6左边的元素确定位置时没必要从数组尾部开始移动,直接从6元素索引-1的位置移动即可。
26-Arrays
没有构造,全是静态方法。
toString
二分查找,数组应该是顺序的
排序,底层是快排
8-4-时间日期类
01-时间概述
世界标准时间:格林威治天文台时间,简称GMT。现在已经有点偏差了,现在标准时间是原子钟提供的时间。
中国时间:世界标准时间+8小时
计算机中的时间原点:1970年1月1日 00:00:00 C语言的生日。了解更多:点击跳转
02-Date类概述和构造方法
Date代表了一个特定的时间,精确到毫秒。
空参构造,表示电脑当前时间。
带参构造,从计算机的时间原点,过了指定毫秒的那个时间
public class DateDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 电脑的当前时间
Date date = new Date();
// Thu May 04 13:36:14 CST 2023
System.out.println(date);
// 计算机的时间原点,过了指定毫秒的那个时间
Date date1 = new Date(0L);
// Thu Jan 01 08:00:00 CST 1970 为什么是8点?东八区
System.out.println(date1);
// 1970年早上九点
Date date2 = new Date(3600*1000);
// Thu Jan 01 09:00:00 CST 1970
System.out.println(date2);
}
}
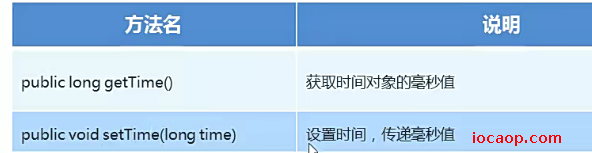
03-Date成员方法
public class DateDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
// Thu May 04 13:42:07 CST 2023
System.out.println(date);
// 获取毫秒数
long time = date.getTime();
// 1683178927205
System.out.println(time);
// 与下面这条等价
System.currentTimeMillis();
// 设置时间毫秒数
date.setTime(0L);
// Thu Jan 01 08:00:00 CST 1970
System.out.println(date);
}
}
04-SimpleDateFormat
可以对Date对象进行格式化和解析。
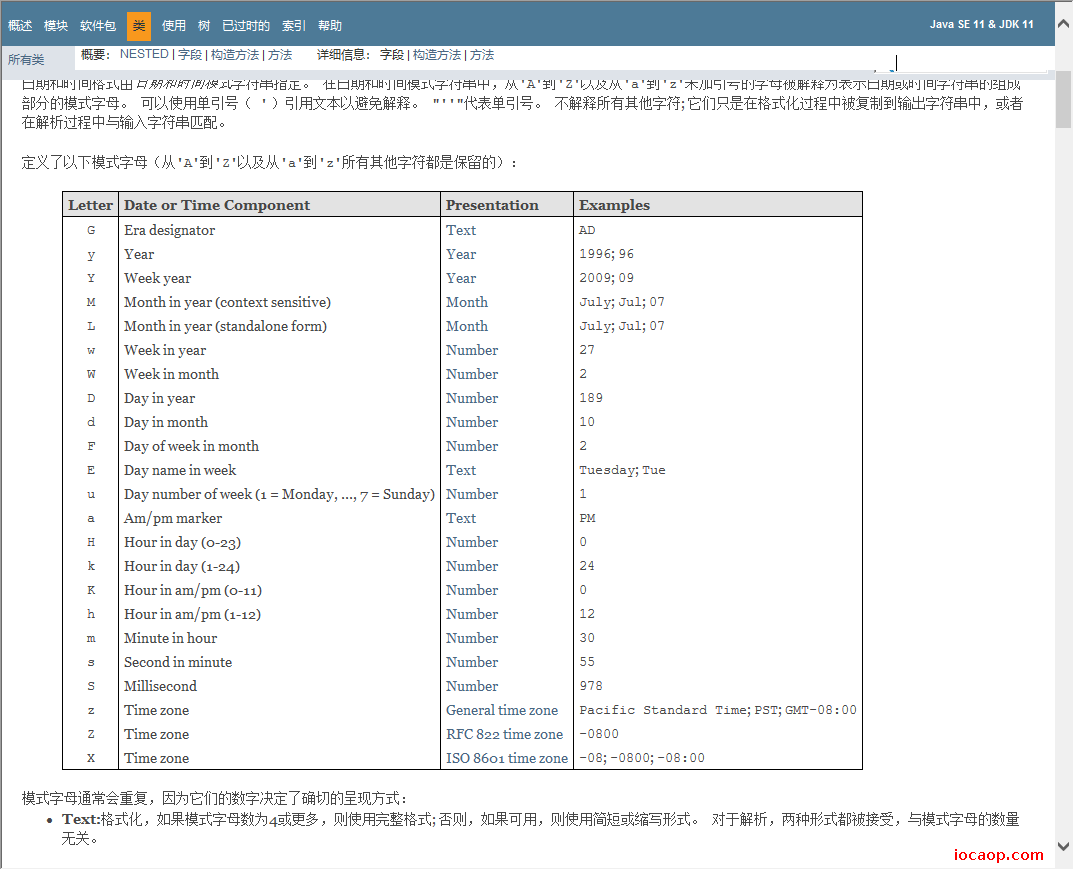
常用模式字母对应关系如下:
- y 年
- M 月
- d 日
- H 时
- m 分
- s 秒
如:
- 2020-11-11 13:27:06 对应模式:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
- 2020年11月11日 13:27:06 对应模式yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss
SimpleDateFormat的构造方法:
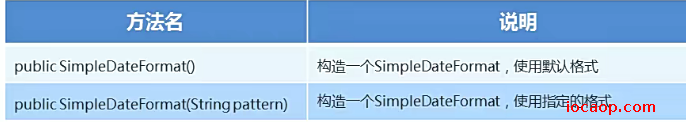
public class DateDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建时间
Date date = new Date();
// 创建日期格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
}
}
创建好了,就需要调用成员方法进行格式化和解析:

public class DateDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建时间
Date date = new Date();
// 创建日期格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
// 格式化
String format = sdf.format(date);
// 2023年05月04日 13:54:56
System.out.println(format);
}
}
反过来也是一样,将字符串解析成Date对象:
需要注意sdf的格式需要和时间字符串格式一致,否则会报异常。
public class DateDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// 创建时间
Date date = new Date();
// 创建日期格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
// 格式化
String format = sdf.format(date);
// 2023年05月04日 13:54:56
System.out.println(format);
// 解析
Date parse = sdf.parse(format);
// Thu May 04 13:56:07 CST 2023
System.out.println(parse);
}
}
05-练习

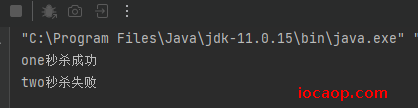
付款时间:2020年11月11日 0:03:47和2020年11月11日 0:10:11哪个秒杀成功?
需要判断时间是否在秒杀范围,如何判断?可以转成毫秒值进行比较。
public class DateDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// 秒杀活动的开始时间和结束时间字符串
String start = "2020年11月11日 0:0:0";
String end = "2020年11月11日 0:10:0";
// 两个下单时间字符串
String one = "2020年11月11日 0:03:47";
String two = "2020年11月11日 0:10:11";
// 创建时间格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
// 解析城Date对象并获取毫秒值
long startTime = sdf.parse(start).getTime();
long endTime = sdf.parse(end).getTime();
long oneTime = sdf.parse(one).getTime();
long twoTime = sdf.parse(two).getTime();
if (oneTime <= endTime && oneTime >= startTime) {
System.out.println("one秒杀成功");
} else {
System.out.println("one秒杀失败");
}
if (twoTime <= endTime && twoTime >= startTime) {
System.out.println("two秒杀成功");
} else {
System.out.println("two秒杀失败");
}
}
}
06-JDK8的体验
假如有字符串表示的时间 2020年11月11日 0:00:00 现在需要将时间往后一天。在jdk7中需要这样做:
在Date类中没有提供相应的方法,需要获取Date对应的毫秒数手动计算进行相加:
private static void jdk7Time() throws ParseException {
String strTime = "2020年11月11日 0:00:00";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
Date date = sdf.parse(strTime);
long time = date.getTime();
date.setTime(time+1000*60*60*24);
// 2020年11月12日 00:00:00
System.out.println(sdf.format(date));
}
而在jdk8中,可以使用LocalDateTime中的方法进行计算:
private static void jdk8Time() {
String strTime = "2020年11月11日 00:00:00";
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(strTime, dateTimeFormatter);
LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.plusDays(1);
String result = newLocalDateTime.format(dateTimeFormatter);
// 2020年11月12日 00:00:00
System.out.println(result);
}
需要注意的是,jdk8格式化要严格一点:保留两位,否则报错。
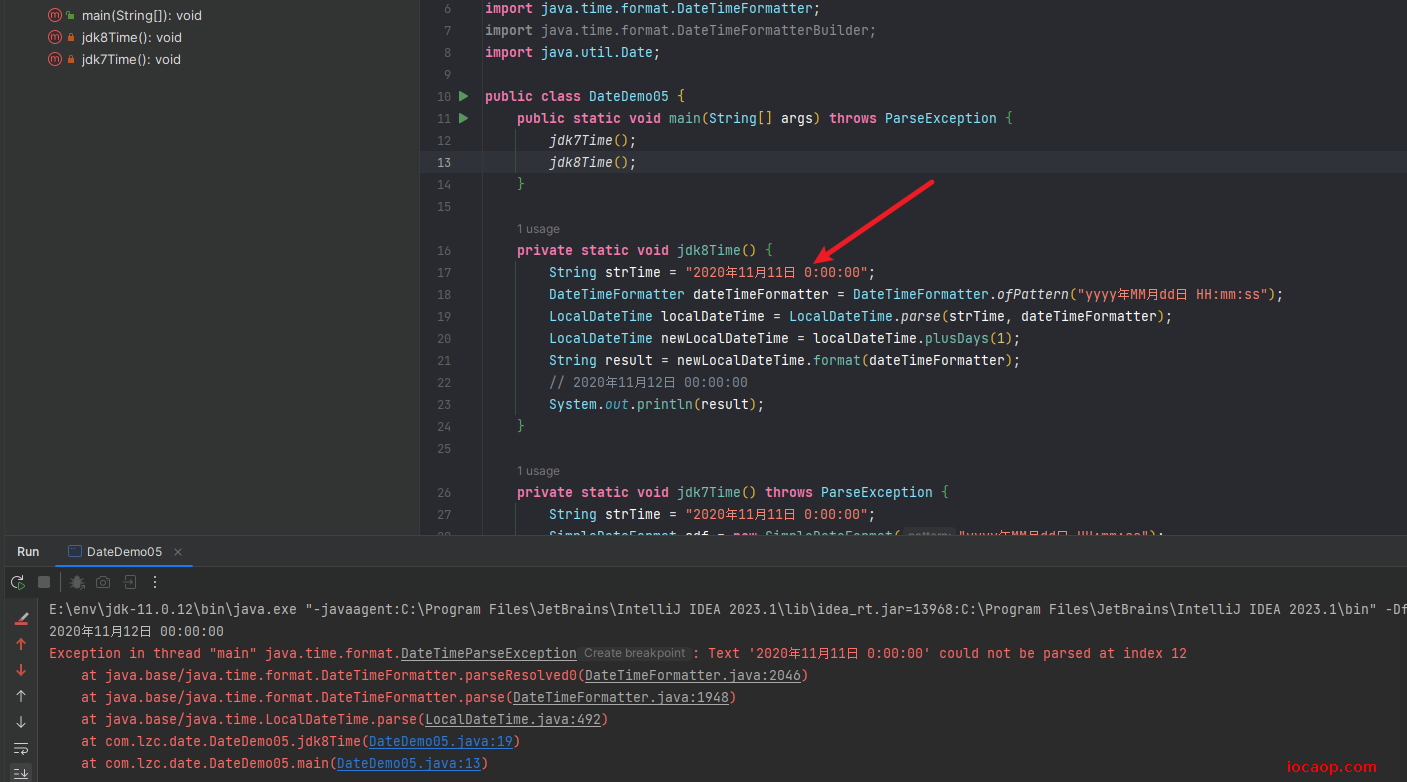
07-JDK8新增时间类-获取时间对象
在jdk8,jdk7中的Date被拆分成了三个类:

public class JDK8DateDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 2023-05-04T23:12:45.785872500
System.out.println(now);
// 如果写错,会报错 如13月 32日 等
LocalDateTime time = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 1, 1, 1);
// 2020-11-11T01:01:01
System.out.println(time);
}
}
08-获取时间中的每个值
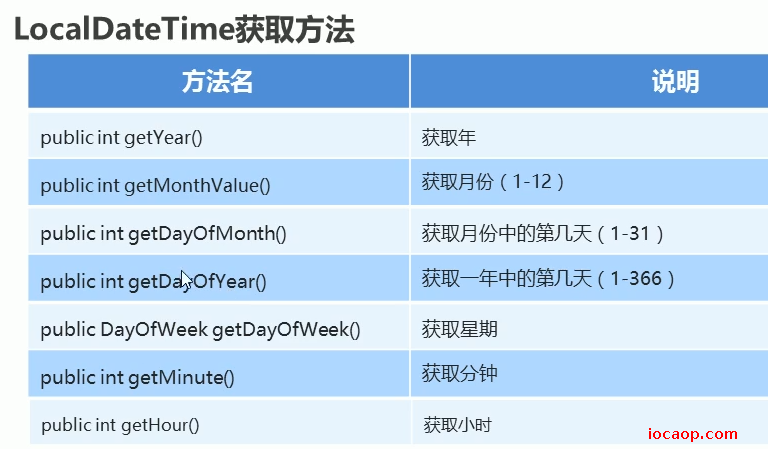
/**
* jdk8 获取时间中的每个值
*
* @author lzc
* @date 2023/05/05
*/
public class JDK8DateDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 11, 11);
// 获取年
int year = localDateTime.getYear();
System.out.println("year = " + year);
// 月
Month month = localDateTime.getMonth();
System.out.println("month = " + month);
int monthValue = localDateTime.getMonthValue();
System.out.println("monthValue = " + monthValue);
// 日
int dayOfMonth = localDateTime.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.println("dayOfMonth = " + dayOfMonth);
// 星期
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = localDateTime.getDayOfWeek();
System.out.println("dayOfWeek = " + dayOfWeek);
int dayOfYear = localDateTime.getDayOfYear();
System.out.println("dayOfYear = " + dayOfYear);
// 小时
int hour = localDateTime.getHour();
System.out.println("hour = " + hour);
//分钟
int minute = localDateTime.getMinute();
System.out.println("minute = " + minute);
}
}
09-时间转换方法
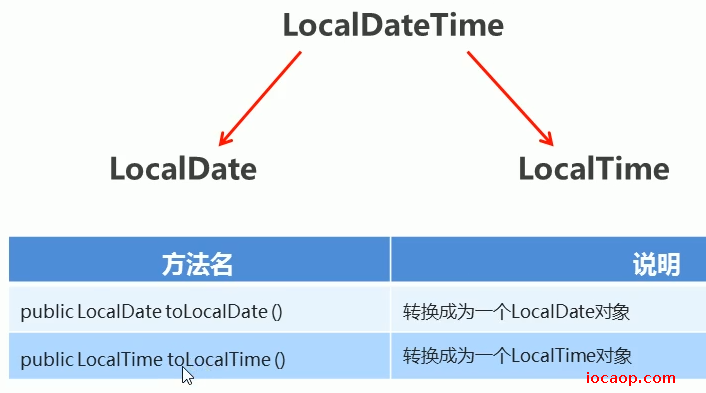
/**
* jdk8 时间转换方法
*
* @author lzc
* @date 2023/05/05
*/
public class JDK8DateDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("now = " + now);
LocalDate localDate = now.toLocalDate();
System.out.println("localDate = " + localDate);
LocalTime localTime = now.toLocalTime();
System.out.println("localTime = " + localTime);
}
}
10-格式化和解析
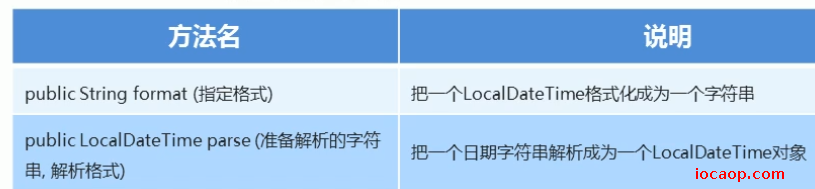
在jdk7中,日期格式化器是SimpleDateFormat,而在jdk8中是DateTimeFormatter

private static void parse() {
String strTime = "2020年11月11日 11:11:11";
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(strTime, dateTimeFormatter);
System.out.println("dateTime = " + dateTime);
}
private static void format() {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 直接输出 now = 2023-05-05T07:22:50.455788700
System.out.println("now = " + now);
// 格式化输出 format = 2023年05月05日 07:22:50
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
String format = now.format(dateTimeFormatter);
System.out.println("format = " + format);
}
11-plus系列方法
public class JDK8DateDemo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime years2024 = now.plusYears(1);
System.out.println("years2024 = " + years2024);
LocalDateTime years2022= now.plusYears(-1);
System.out.println("years2022 = " + years2022);
}
}
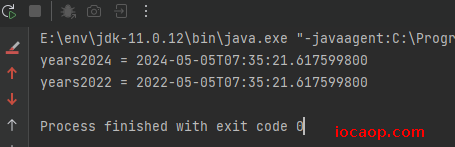
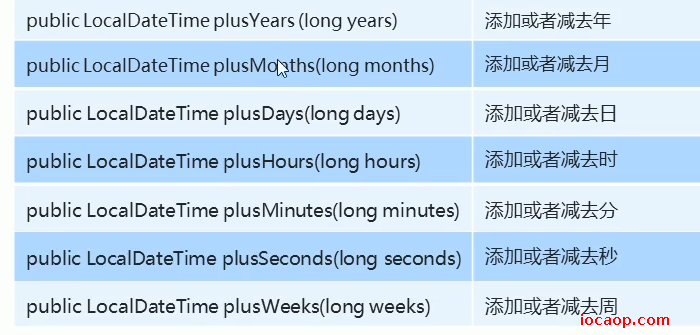
需要注意的就是,参数可以是正数也可以是负数。正数则往后一年,负数则是前一年。
类似方法:
12-minus系列方法
与plus方法相反,用法一样。一个加,一个减。
public class JDK8DateDemo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime year2022 = now.minusYears(1);
System.out.println("year2022 = " + year2022);
LocalDateTime year2024 = now.minusYears(-1);
System.out.println("year2024 = " + year2024);
}
}
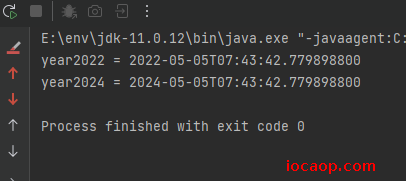
参数是正数则是以前的时间,为负数则是以后的时间。
类似的方法还有:
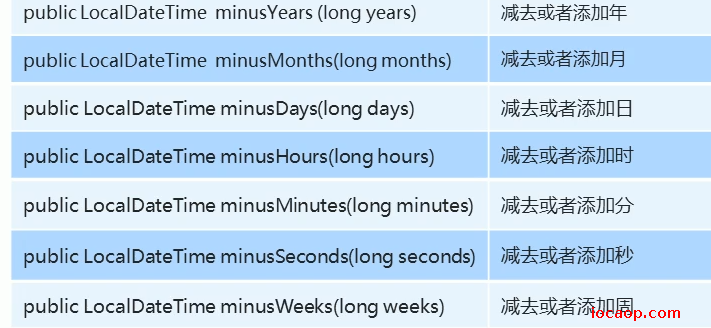
13-with系列方法
直接修改时间
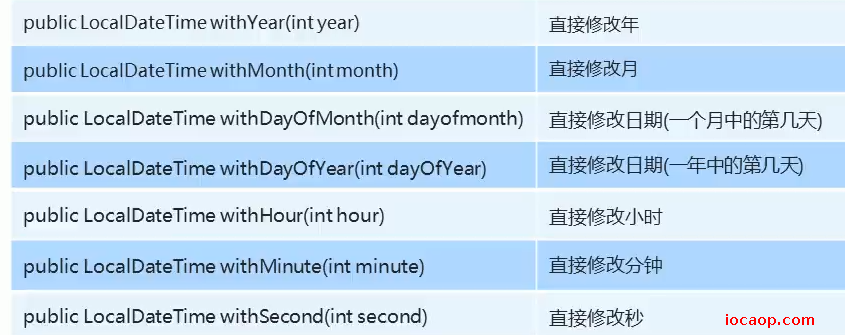
public class JDK8DateDemo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("now = " + now);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = now.withYear(2222);
System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = now.withMonth(20);
}
}
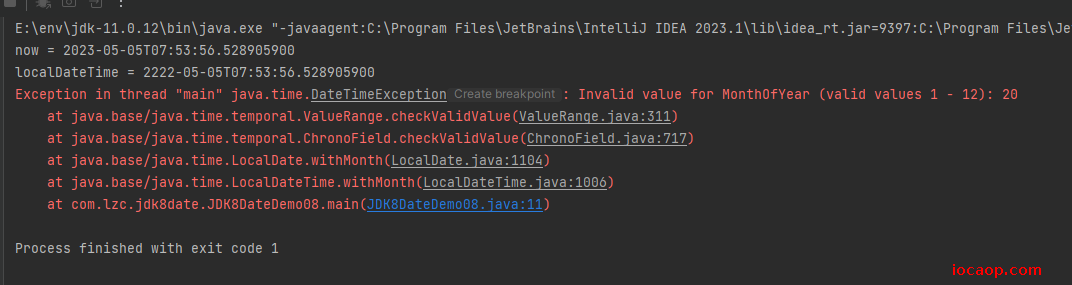
需要注意,如果超出范围,会报异常。plus、minus、with方法不会修改原来的对象,而是返回一个新的时间对象,原来的对象还是原来的时间
14-时间间隔对象
Period
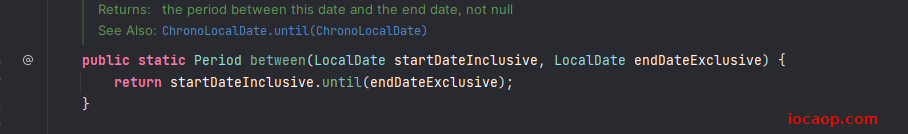
传入两个
LocalDate对象,获得时间间隔public class JDK8DateDemo09 { public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDate now = LocalDate.now(); LocalDate localDate2022 = LocalDate.of(2020, 11, 11); Period period = Period.between(localDate2022, now); // period = P2Y5M24D System.out.println("period = " + period); // 获得间隔的年数 int years = period.getYears(); System.out.println("years = " + years); // 获得间隔的月数 int months = period.getMonths(); System.out.println("months = " + months); // 获得间隔的天数 int days = period.getDays(); System.out.println("days = " + days); } }Duration
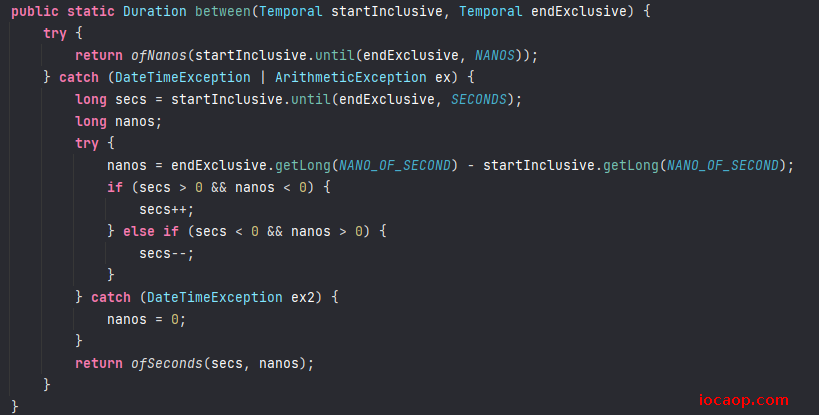
public class JDK8DateDemo10 { public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now(); LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11); Duration duration = Duration.between(now, localDateTime); // duration = PT-21717H-23M-19.7687483S System.out.println("duration = " + duration); // 获得间隔的秒 long seconds = duration.toSeconds(); System.out.println("seconds = " + seconds); // 获得间隔的微秒 long millis = duration.toMillis(); System.out.println("millis = " + millis); // 获得间隔的纳秒 long nanos = duration.toNanos(); System.out.println("nanos = " + nanos); } }其他方法:
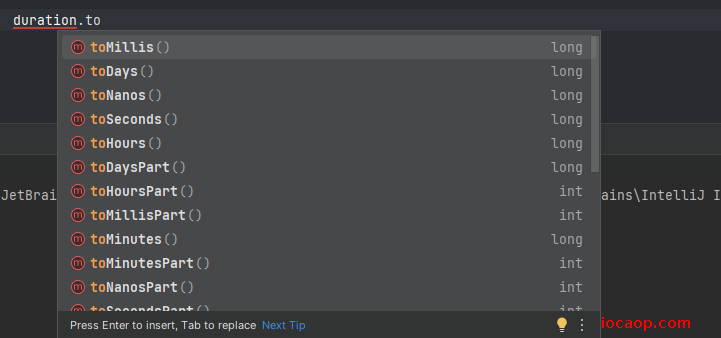
8-5-异常
16-异常的体系和异常的分类
异常:程序中出现了不正常的情况,程序在执行过程中出现非正常的情况,最终会导致jvm非正常停止。
注意:语法错误不算在异常体系中。
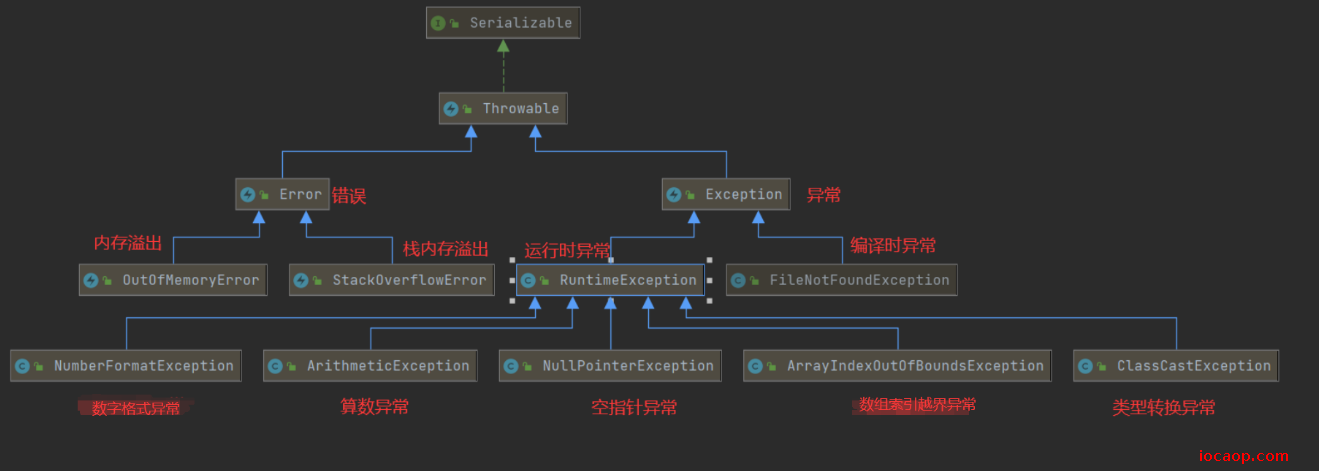
- Error:严重问题,通过代码无法处理,比如内存溢出
- Exception:称为异常类,表示程序本身可以处理的问题
- RuntimeException及其子类:运行时异常。(空指针异常,数组越界异常)。
- 除RuntimeException之外所有的异常:编译期间必须处理的,否则程序不能通过编译。
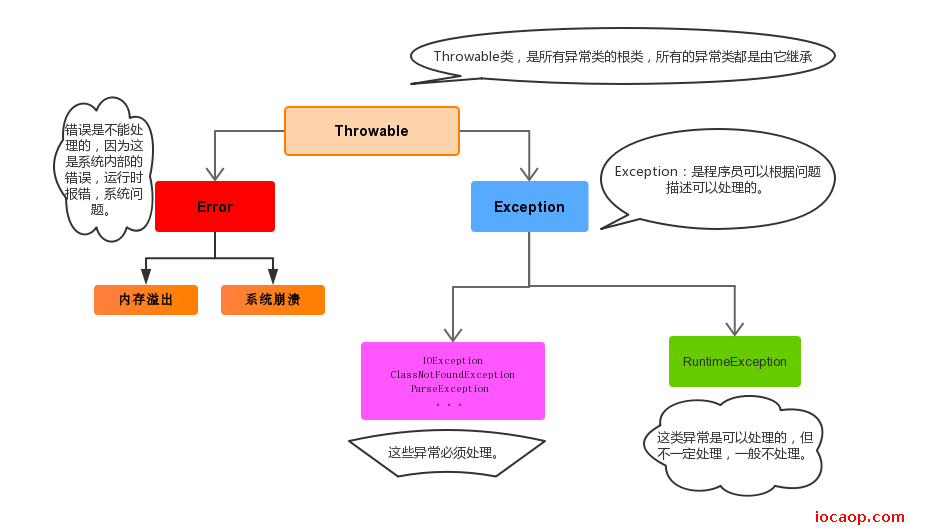
运行时异常和编译时异常:

17-虚拟机默认处理异常的方式
思考:为什么出现异常时,控制台会出现红色警告?
在出现异常时,出现什么异常,就会在出现异常的位置创建对应的异常对象。
创建完异常对象后:
- 首先会看程序中有没有自己处理异常的代码
- 如果么有就交给本方法的调用者处理
- 如果还是没有,最终这个异常交给虚拟机默认处理
- JVM默认处理异常做了什么?
JVM默认处理异常:
- 将异常名称、异常信息、异常出现的位置等信息以红色字体输出在控制台
- 停止程序运行。(哪里出现异常,程序就在哪里停止)
18-throws声明异常
/**
* 异常demo06
*
* @author 赖卓成
* @date 2023/05/05
*/
public class ExceptionDemo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
method1();
// 如果出现异常,不处理,则会交给虚拟机默认处理
method2();
}
/**
*
* @throws ParseException 用于告知调用者,调用该方法将会出现异常,如果没有出现,程序照常运行,如果出现异常,异常由调用者处理
*/
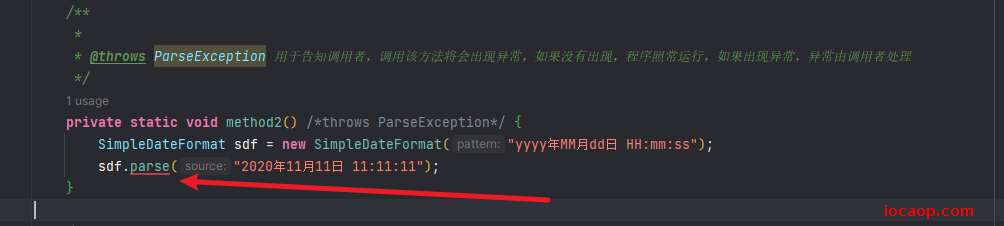
private static void method2() throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
sdf.parse("2020年11月11日 11:11:11");
}
/**
*
* @throws NullPointerException 用于告知调用者,调用该方法将会出现异常,如果没有出现,程序照常运行,如果出现异常,异常由调用者处理
*/
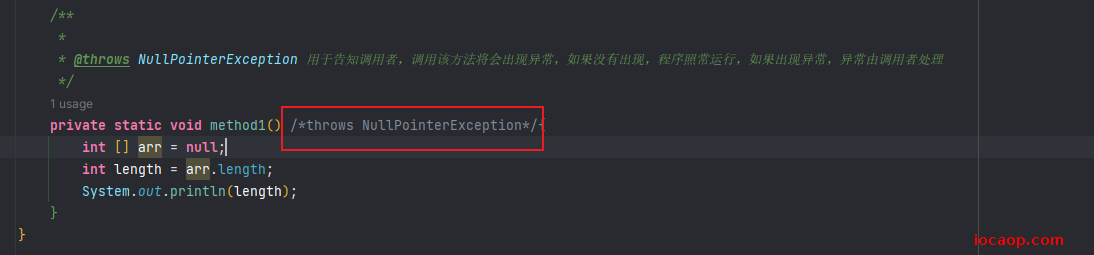
private static void method1() throws NullPointerException{
int [] arr = null;
int length = arr.length;
System.out.println(length);
}
}
19-声明异常的注意事项
如果是运行时异常,throws可以省略不写,如果是编译时异常,则必须要写。
运行时异常,省略不写,没问题:
编译时异常,省略不写,报红,必须手动throws:
20-throw抛出异常
/**
* 异常demo01
*
* @author 赖卓成
* @date 2023/05/05
*/
public class ExceptionDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("哈哈哈1");
System.out.println("哈哈哈2");
System.out.println("哈哈哈3");
// 代码执行到这,手动抛出了运行时异常,并且自己没有处理,交给了jvm默认处理。下面的代码不会再执行,且编译会提示无法访问的语句
throw new RuntimeException();
System.out.println("哈哈哈4");
}
}
throws和throw区别
throws:
- 用在方法声明后面,跟的是异常类名
- 表示声明异常,告知调用者,调用该方法可能会出现这样的异常
throw:
- 用在方法体内,跟的是异常对象名。
- 表示手动抛出异常对象,由方法体内的语句处理。
抛出异常的意义:
- 在方法中,如果出现业务错误或参数错误,没有继续运行下去的意义,则采取抛出处理,让改方法结束。
- 告知调用者该方法出现了问题。
public class ExceptionDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] arr = null;
printArr(arr);
}
private static void printArr(int[] arr) {
if (Objects.isNull(arr)){
throw new RuntimeException("数组不能为null");
}
System.out.println("Arrays.toString(arr) = " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
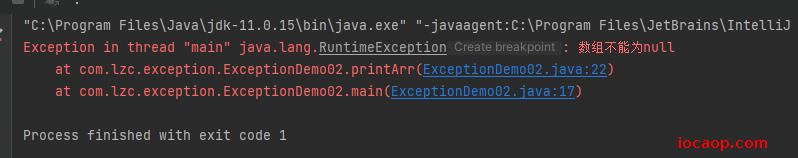
21-try...catch
目的:为了让程序继续往下执行。
/**
* 异常demo02
*
* @author 赖卓成
* @date 2023/05/05
*/
public class ExceptionDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] arr = null;
// 自己处理异常,目的就是为了让代码不终止,继续往下执行。
try{
// 有可能出现异常的代码
printArr(arr);
}catch (RuntimeException e){
// 如果出现异常,打印一句话
System.out.println("参数不能为null");
}
// 测试后面的代码会不会执行
System.out.println("哈哈哈");
}
private static void printArr(int[] arr) {
if (Objects.isNull(arr)){
throw new RuntimeException("数组不能为null");
}
System.out.println("Arrays.toString(arr) = " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
22-try...catch常见问题
如果try中没有遇到问题,怎么执行?
public class ExceptionDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String line = scanner.nextLine(); int i = Integer.parseInt(line); System.out.println(i); System.out.println("测试123"); }catch (NumberFormatException e){ System.out.println("出现异常咯"); } System.out.println("测试456"); } }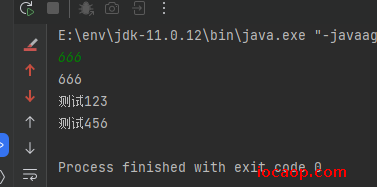
正常执行,把try中的代码执行完,再执行try...catch体系外的代码,catch中的代码不会执行。
如果try中遇到了问题,那么try下面的代码还会执行吗?
和上面一样的代码。
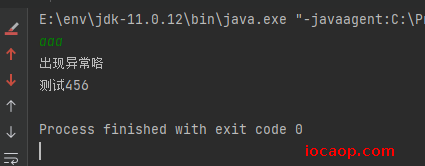
try中,出现异常的代码后面的都不执行了,跳到catch块中执行,执行完以后再执行try...catch体系外的代码
如果出现的问题没有被捕获,那么程序如何运行?
public class ExceptionDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String line = scanner.nextLine(); int i = Integer.parseInt(line); System.out.println(i); System.out.println("测试123"); }catch (NullPointerException e){ System.out.println("出现异常咯"); } System.out.println("测试456"); } }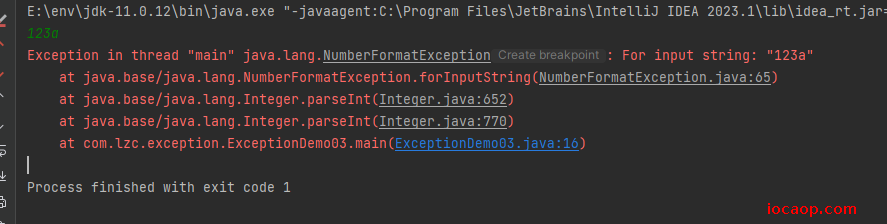
没有被捕获,则会交给虚拟机默认处理
同时有可能出现多个异常,怎么处理?
public class ExceptionDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String line = scanner.nextLine(); int i = Integer.parseInt(line); System.out.println(i); System.out.println(i/0); System.out.println("测试123"); }catch (NumberFormatException e){ System.out.println("出现number异常咯"); }catch (ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println("出现zero异常咯"); } System.out.println("测试456"); } }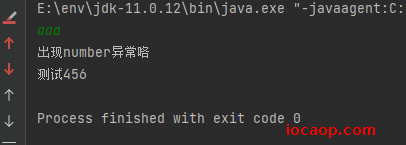
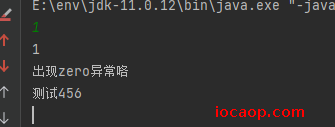
需要多个catch块来捕获,或者直接捕获父类异常
Exception,但需要根据实际业务来捕获,是否需要分情况处理异常。
23-Throwable的成员方法
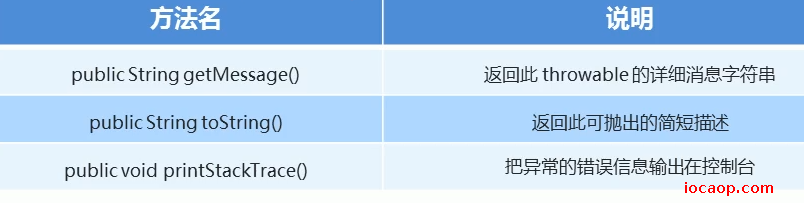
这是异常的最顶级父类的成员方法,所以所有的异常都可以调用这三个方法。
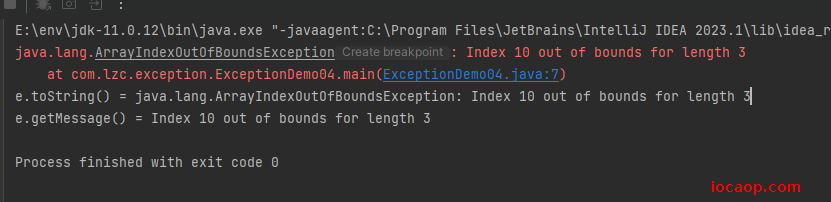
public class ExceptionDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int [] arr = {1,2,3};
System.out.println("arr[10] = " + arr[10]);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 这不是虚拟机异常默认处理方式,打印完后,下面的代码还会执行
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("e.toString() = " + e.toString());
System.out.println("e.getMessage() = " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
选定代码后可以按快捷键ctrl+alt+t快捷生成try...catch代码块
24-异常的小练习
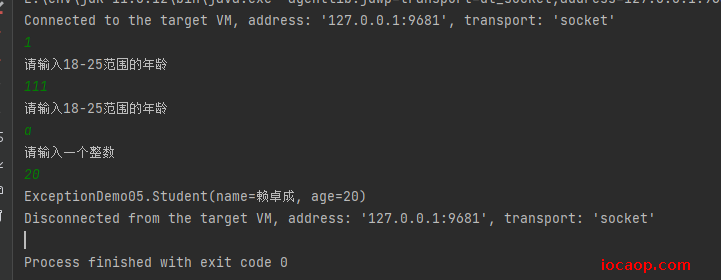
需求:键盘录入学生的姓名和年龄,其中年龄为18-25岁,超出这个范围是异常数据,不能赋值,需要重新录入,一直到录入正确为止。
public class ExceptionDemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("赖卓成");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
int age = 0;
try {
age = Integer.parseInt(line);
if (age < 18 || age > 25) {
throw new RuntimeException("请输入18-25范围的年龄");
}
} catch (NumberFormatException numberFormatException) {
System.out.println("请输入一个整数");
continue;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
continue;
}
student.setAge(age);
System.out.println(student);
break;
}
}
@Data
static class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
}
25-自定义异常
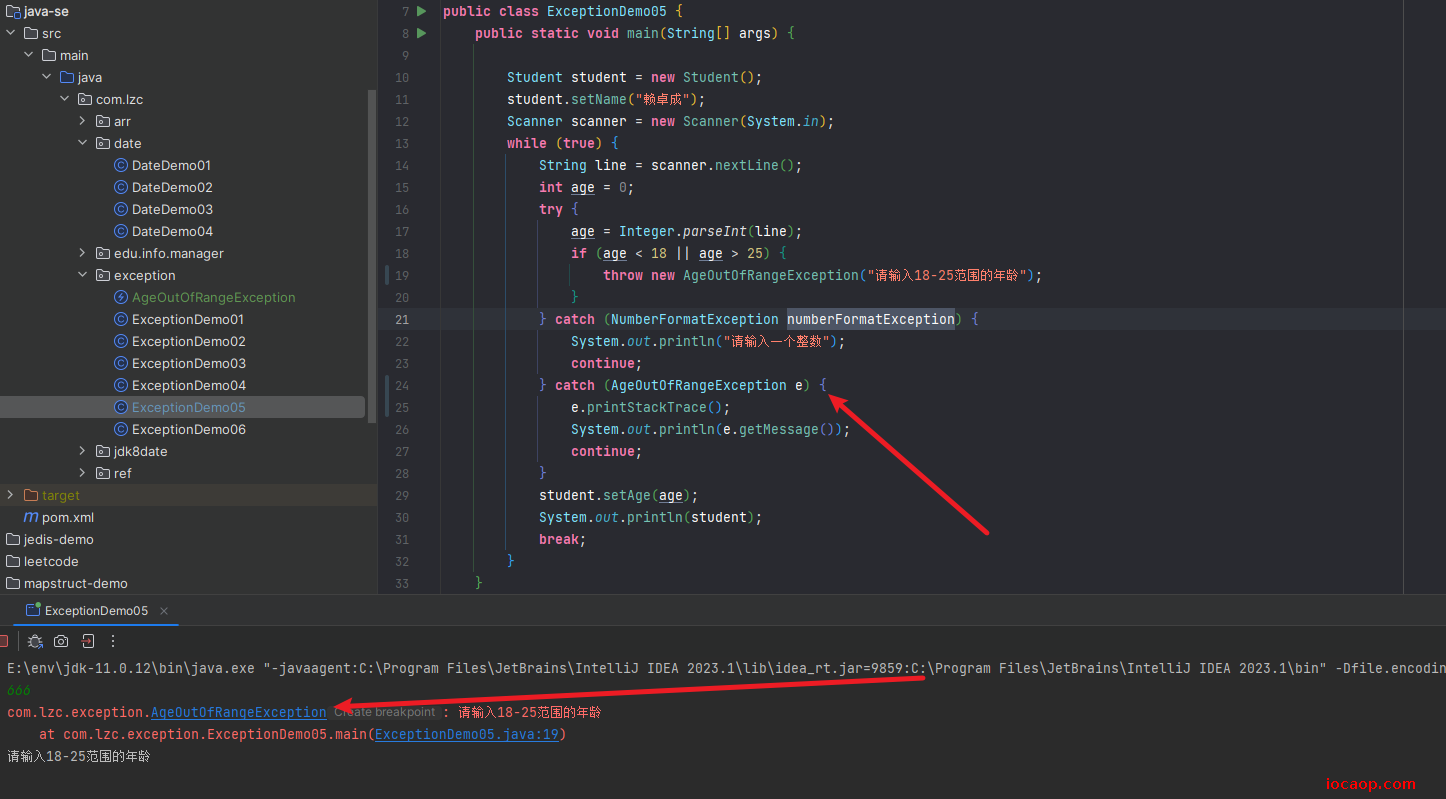
上面练习的例子中,当年龄超出范围时,抛出的是RuntimeException,范围太大了,需要自定义异常。
自定义异常需要继承RuntimeException,只需要定义好构造方法就行了,如果有其他字段需求,可以增加,如异常码、异常信息等。
public class AgeOutOfRangeException extends RuntimeException{
public AgeOutOfRangeException() {
}
public AgeOutOfRangeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}